可靠性保障机制
Memfit AI 实现了多层纵深防御策略,确保在不可预测的环境中稳定运行。与遇错即崩的脆弱脚本不同,系统被设计为优雅降级、自主恢复、从错误中学习。本文档全面介绍 Memfit AI 架构中实现的可靠性机制。
理论基础
Memfit AI 的可靠性框架建立在分布式系统、认知科学和控制理论的几个既定原则之上:
- 优雅降级:部分故障发生时系统继续以降低的能力运行,而非灾难性崩溃。
- 自适应控制:实时反馈回路使系统能够根据观察到的结果调整行为。
- 元认知:智能体能够推理自己的推理过程,实现自我修正。
- 累积学习:每次失败都为不断增长的知识库做出贡献,提高未来的可靠性。
1. 自适应自我反思
自我反思是系统的"免疫系统"。它不是独立的后处理过程,而是执行循环的组成部分,深度嵌入 reactloops 架构中。
1.1 反思级别分类
系统实现了分级的反思强度层次结构,每个级别具有不同的计算成本和诊断能力:
| 级别 | 名称 | 触发条件 | AI 参与 | 记忆搜索深度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | None | 禁用反思 | 无 | 无 |
| 1 | Minimal | 简单动作的默认值 | 无(仅记录) | 无 |
| 2 | Standard | SPIN 检测、迭代 > 5 | 是 | 2 KB |
| 3 | Deep | 复杂动作分析 | 是 | 5 KB |
| 4 | Critical | 动作执行失败 | 是 | 10 KB |
反思级别根据多种因素动态确定:
// ReflectionLevel 层次结构(来自 action_reflection.go)
type ReflectionLevel int
const (
ReflectionLevel_None ReflectionLevel = iota
ReflectionLevel_Minimal // 仅记录执行结果
ReflectionLevel_Standard // 评估基本影响
ReflectionLevel_Deep // 详细环境分析
ReflectionLevel_Critical // 失败场景的根因分析
)
1.2 触发机制
系统实时监控执行并通过复杂的决策树在特定条件下触发反思:
1.2.1 主要触发器:执行失败
当动作以错误终止时,系统立即升级到 Critical 反思级别:
// 来自 reflection.go - shouldTriggerReflection
isTerminated, err := operator.IsTerminated()
if isTerminated && err != nil {
// 失败场景:触发关键反思
log.Infof("action[%s] failed, trigger critical reflection", action.ActionType)
return ReflectionLevel_Critical
}
1.2.2 次要触发器:迭代阈值
在未完成任务的情况下执行 5 次迭代后,系统进入增强监控状态:
// 高迭代次数:间隔反思策略(5 次之后才开始)
if iterationCount > 5 {
// 优先检查 SPIN 情况
if r.IsInSameActionTypeSpin() {
log.Infof("SPIN detected at iteration[%d], trigger immediate reflection", iterationCount)
return ReflectionLevel_Standard
}
// 非反思轮次:仅最小反思
return ReflectionLevel_Minimal
}
1.2.3 第三触发器:操作者定义的升级
单个动作处理器可以通过操作者接口请求特定的反思级别:
operatorLevel := operator.GetReflectionLevel()
if operatorLevel != ReflectionLevel_None {
log.Infof("use action-defined reflection level: %s", operatorLevel.String())
return operatorLevel
}
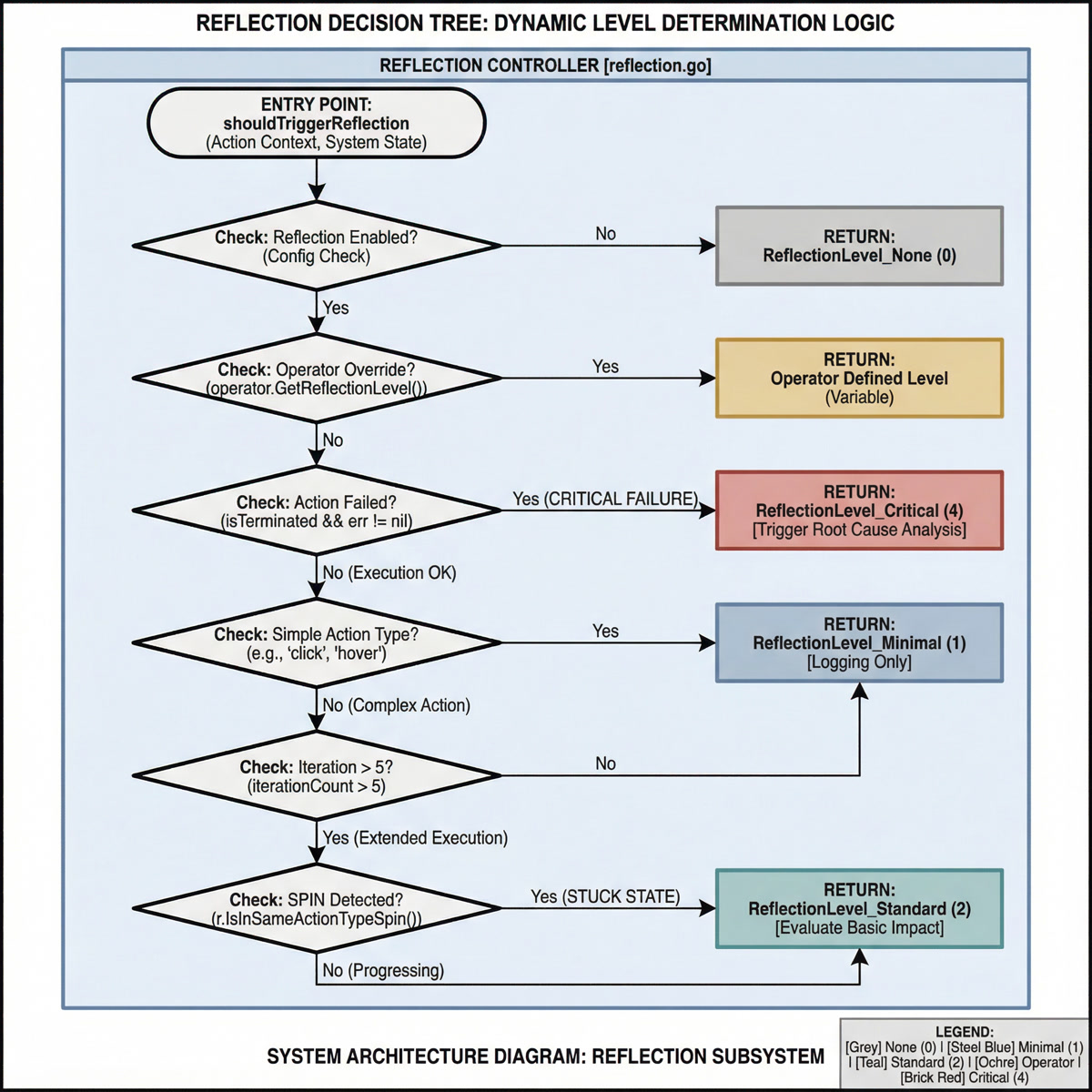
[图表占位符:反思决策树]
- 布局: 自上而下的决策流程图
- 节点:
- 入口点 (shouldTriggerReflection)
- 检查:反思已启用? → 否 → 返回 None
- 检查:操作者覆盖? → 是 → 返回操作者级别
- 检查:动作失败? → 是 → 返回 Critical
- 检查:简单动作? → 是 → 返回 Minimal
- 检查:迭代 > 5? → 是 → 检查 SPIN → Standard/Minimal
- 默认 → 返回 Minimal
- 关键要点: 展示触发条件的层次优先级。
1.3 反思执行管道
当触发反思时,系统执行多阶段管道:
阶段 1:数据收集
系统捕获当前执行状态的综合快照:
// ActionReflection 结构体(来自 action_reflection.go)
type ActionReflection struct {
// 基本信息
ActionType string `json:"action_type"`
ActionParams map[string]interface{} `json:"action_params"`
ExecutionTime time.Duration `json:"execution_time"`
IterationNum int `json:"iteration_num"`
Success bool `json:"success"`
ErrorMessage string `json:"error_message,omitempty"`
// 环境影响分析
EnvironmentalImpact *EnvironmentalImpact `json:"environmental_impact,omitempty"`
// 反思输出
Suggestions []string `json:"suggestions,omitempty"`
ReflectionLevel string `json:"reflection_level"`
ReflectionTimestamp time.Time `json:"reflection_timestamp"`
// SPIN 检测集成
IsSpinning bool `json:"is_spinning,omitempty"`
SpinReason string `json:"spin_reason,omitempty"`
}
阶段 2:环境影响分析
对于 Standard 级别及以上,系统分析已执行动作的环境影响:
// EnvironmentalImpact 结构体(来自 action_reflection.go)
type EnvironmentalImpact struct {
StateChanges []string `json:"state_changes"`
ResourceUsage map[string]interface{} `json:"resource_usage"`
SideEffects []string `json:"side_effects"`
PositiveEffects []string `json:"positive_effects"`
NegativeEffects []string `json:"negative_effects"`
}
此分析捕获:
- 状态变化:动作是继续还是终止了循环
- 资源使用:消耗的计算资源
- 副作用:外部系统修改
- 影响分类:对任务进度的正面和负面影响
阶段 3:记忆增强的 AI 分析
对于 Standard 级别及以上,系统调用带有历史上下文的 AI 辅助分析:
// 记忆搜索深度因反思级别而异(来自 reflection_memory.go)
switch level {
case ReflectionLevel_Minimal:
return "" // 最小级别不搜索记忆
case ReflectionLevel_Standard:
searchSizeLimit = 2 * 1024 // 2KB
case ReflectionLevel_Deep:
searchSizeLimit = 5 * 1024 // 5KB
case ReflectionLevel_Critical:
searchSizeLimit = 10 * 1024 // 10KB - 关键反思需要更多上下文
}
查询构建经过语义优化:
// 根据动作上下文构建搜索查询
query := fmt.Sprintf("action '%s' execution analysis failure success pattern",
reflection.ActionType)
if !reflection.Success && reflection.ErrorMessage != "" {
query += " " + reflection.ErrorMessage
}
阶段 4:时间线注入
反思结果使用强调性语言注入时间线,以确保 AI 智能体优先考虑指导:
// 来自 reflection_memory.go - addReflectionToTimeline
if reflection.Success {
timelineMsg.WriteString(fmt.Sprintf("✓ [REFLECTION] Action '%s' EXECUTED SUCCESSFULLY",
reflection.ActionType))
} else {
timelineMsg.WriteString(fmt.Sprintf("✗ [CRITICAL REFLECTION] Action '%s' FAILED",
reflection.ActionType))
}
// 使用强语气的强制建议
if len(reflection.Suggestions) > 0 {
timelineMsg.WriteString("MANDATORY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR FUTURE ACTIONS:\n")
for i, suggestion := range reflection.Suggestions {
timelineMsg.WriteString(fmt.Sprintf("%d. %s\n", i+1, suggestion))
}
}
阶段 5:反思缓存
最近的反思被缓存用于提示上下文(限制为最近 3 条):
// 缓存最近的反思用于提示上下文
reflections = append(reflections, reflection)
if len(reflections) > 3 {
reflections = reflections[len(reflections)-3:]
}
r.Set("self_reflections", reflections)
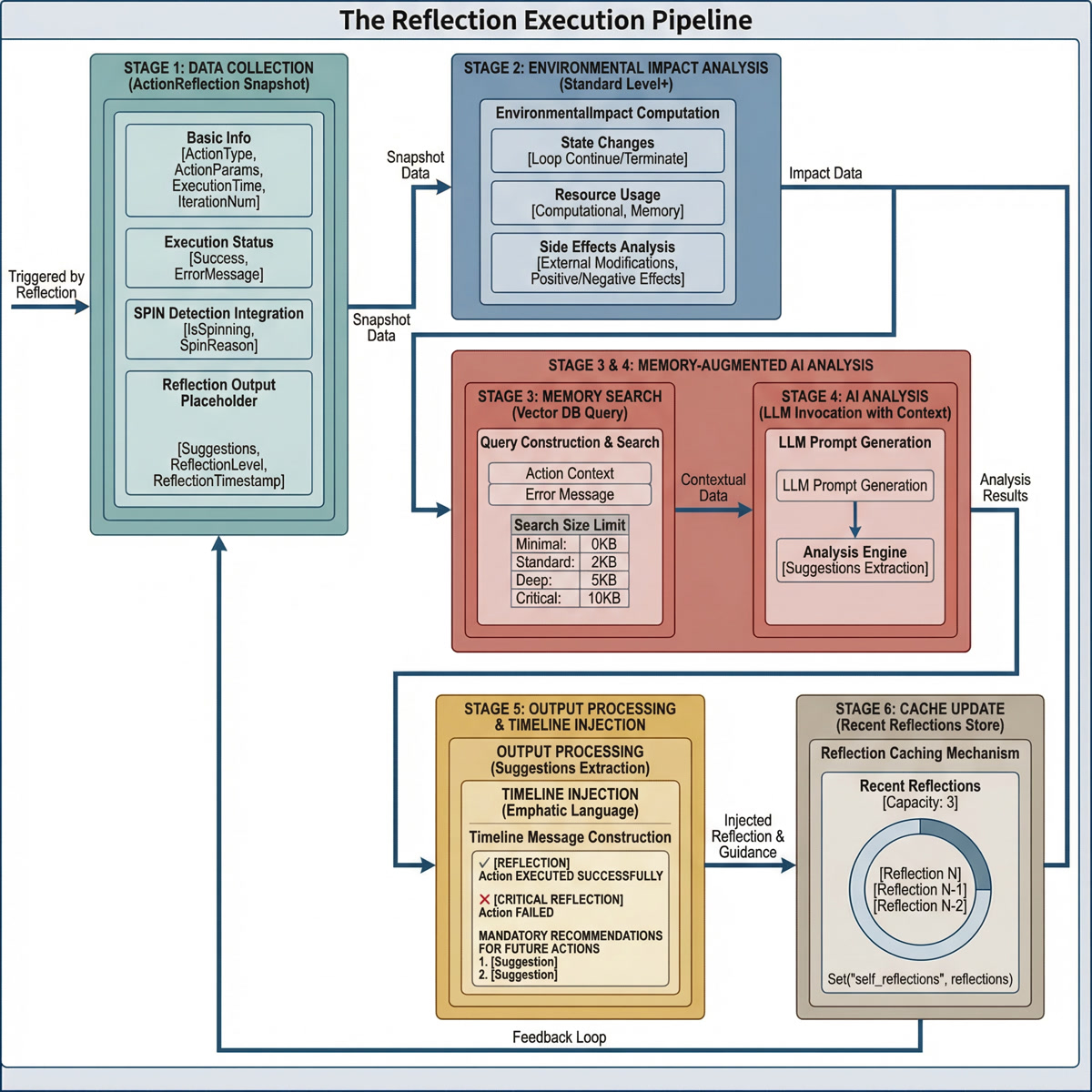
[图表占位符:反思管道]
- 布局: 带并行分支的从左到右管道
- 阶段:
- 数据收集 (ActionReflection 快照)
- 环境分析 (EnvironmentalImpact 计算)
- 记忆搜索 (向量数据库查询)
- AI 分析 (带上下文的 LLM 调用)
- 输出处理 (建议提取)
- 时间线注入 (高优先级上下文)
- 缓存更新 (最近反思存储)
- 关键要点: 演示综合的多阶段反思过程。
2. SPIN 检测与防循环
LLM 智能体最常见的失败之一是陷入无限循环(例如,当权限被拒绝时反复尝试 cat /etc/passwd)。Memfit AI 采用双层检测系统,结合启发式和语义分析。
2.1 第一层:动作类型 SPIN 检测(启发式)
这种低成本检测机制无需 AI 参与即可运行:
2.1.1 检测算法
// 来自 spin_detection.go - IsInSameActionTypeSpin
func (r *ReActLoop) IsInSameActionTypeSpin() bool {
r.actionHistoryMutex.Lock()
defer r.actionHistoryMutex.Unlock()
threshold := r.sameActionTypeSpinThreshold
if threshold <= 0 {
threshold = 3 // 默认阈值
}
historyLen := len(r.actionHistory)
if historyLen < threshold {
return false
}
// 检查最近 N 次动作是否都是相同类型
lastActionType := r.actionHistory[historyLen-1].ActionType
for i := historyLen - threshold; i < historyLen; i++ {
if r.actionHistory[i].ActionType != lastActionType {
return false
}
}
log.Infof("detected same action type spin: %d consecutive actions of type %s",
threshold, lastActionType)
return true
}
2.1.2 响应策略
当第一层检测触发时,系统生成即时反馈:
// SpinDetectionResult 结构体
type SpinDetectionResult struct {
IsSpinning bool `json:"is_spinning"`
Reason string `json:"reason"`
Suggestions []string `json:"suggestions"`
NextActions []string `json:"next_actions"`
ActionType string `json:"action_type"`
ConsecutiveCount int `json:"consecutive_count"`
}
// 第一层检测的默认建议
Suggestions: []string{
"尝试使用不同的 Action 类型",
"检查任务目标是否明确",
"考虑是否需要用户澄清",
}
2.2 第二层:逻辑 SPIN 检测(语义)
当第一层触发时,系统升级到 AI 驱动的语义分析:
2.2.1 深度分析调用
// 来自 spin_detection.go - IsInSameLogicSpinWithAI
func (r *ReActLoop) IsInSameLogicSpinWithAI() (*SpinDetectionResult, error) {
// 获取动作历史
recentActions := make([]*ActionRecord, r.sameLogicSpinThreshold)
copy(recentActions, r.actionHistory[historyLen-r.sameLogicSpinThreshold:])
// 获取时间线上下文用于分析
timelineContent := r.getTimelineContentForSpinDetection()
// 构建分析提示
prompt := r.buildSpinDetectionPrompt(recentActions, timelineContent)
// 使用结构化输出模式调用 AI
outputSchema := []aitool.ToolOption{
aitool.WithBoolParam("is_spinning",
aitool.WithParam_Description("是否发生了 SPIN 情况")),
aitool.WithStringParam("reason",
aitool.WithParam_Description("如果发生了 SPIN,说明原因")),
aitool.WithStringArrayParam("suggestions",
aitool.WithParam_Description("提供打破循环的建议")),
aitool.WithStringArrayParam("next_actions",
aitool.WithParam_Description("具体的下一步操作建议")),
}
action, err := r.invoker.InvokeLiteForge(ctx, "spin_detection", prompt, outputSchema)
// ... 处理结果
}
2.2.2 上下文丰富的提示构建
AI 分析接收综合上下文:
// 来自 spin_detection.go - buildSpinDetectionPrompt
prompt.WriteString("你是一个 AI Agent 行为分析专家。请分析以下 Action 执行历史,判断是否发生了 SPIN 情况。\n\n")
prompt.WriteString("SPIN 的定义:AI Agent 反复做出相同或相似的决策,没有让任务得到推进。\n\n")
// 包含详细的动作历史
for i, action := range actions {
prompt.WriteString(fmt.Sprintf("### 第 %d 次执行 (迭代 %d)\n", i+1, action.IterationIndex))
prompt.WriteString(fmt.Sprintf("- Action 类型: %s\n", action.ActionType))
prompt.WriteString(fmt.Sprintf("- Action 名称: %s\n", action.ActionName))
prompt.WriteString("- Action 参数:\n")
// ... JSON 格式化参数
}
// 包含时间线上下文
if timelineContent != "" {
prompt.WriteString("## Timeline 上下文\n\n")
prompt.WriteString(timelineContent)
}
2.3 第三层:领域特定 SPIN 检测
对于代码修改等专门场景,系统采用额外的启发式:
2.3.1 代码修改 SPIN 检测
// 来自 loop_yaklangcode/spin_detection.go
type ModifyRecord struct {
StartLine int
EndLine int
Content string
}
// 区域接近度检查(±5 行)
func isInSameRegion(r1, r2 ModifyRecord) bool {
startDistance := absInt(r1.StartLine - r2.StartLine)
endDistance := absInt(r1.EndLine - r2.EndLine)
return startDistance <= 5 && endDistance <= 5
}
// 小幅编辑检测(≤3 行)
func isSmallEdit(record ModifyRecord) bool {
lineCount := record.EndLine - record.StartLine + 1
return lineCount <= 3
}
2.3.2 SPIN 检测算法
检测算法跟踪修改模式:
// 检测逻辑(来自 loop_yaklangcode/spin_detection.go)
func detectSpinning(loop LoopActionHistoryProvider, currentRecord ModifyRecord) (bool, string) {
// 跨迭代跟踪 spin 计数
spinCount := parseSpinCount(loop.Get("modify_spin_count"))
// 分析最近的 modify_code 动作
historyRecords := extractModifyRecords(loop.GetLastNAction(10))
// 检查同一区域的重复修改
isSameRegion := false
isSmallChange := isSmallEdit(currentRecord)
if len(historyRecords) > 0 {
lastRecord := historyRecords[len(historyRecords)-1]
if isInSameRegion(currentRecord, lastRecord) {
isSameRegion = true
}
}
// SPIN 检测:同一区域 + 小幅更改
if isSameRegion && isSmallChange {
spinCount++
if spinCount >= 3 {
reason := fmt.Sprintf("检测到在第 %d-%d 行附近连续 %d 次小幅修改代码,可能陷入了修改循环",
currentRecord.StartLine, currentRecord.EndLine, spinCount)
return true, reason
}
} else {
spinCount = 0 // 显著更改时重置
}
return false, ""
}
2.3.3 针对性干预提示
当检测到代码修改 spin 时,生成专门的反思提示:
// 来自 loop_yaklangcode/spin_detection.go - generateReflectionPrompt
func generateReflectionPrompt(record ModifyRecord, reason string) string {
return fmt.Sprintf(`【代码修改空转警告】
%s
请停下来进行反思,回答以下问题:
【问题1:改动价值】
本次修改第 %d-%d 行的目标是什么?与上几次修改相比,有什么新的价值或进展?
【问题2:备选路径】
如果不继续修改这几行代码,还有哪些其他解决方案?
请至少列出 3 个不同层面的策略:
- 数据/变量层面的调整
- 算法/逻辑层面的重构
- 接口/API 调用方式的改变
- 使用不同的库或工具函数
【问题3:搜索建议】
强烈建议在继续修改前,先执行以下搜索以寻找正确的代码模式...
【行动建议】
请选择收益最高、风险最低的一个策略,并说明理由。
不要再继续在同一位置反复尝试小幅修改!`,
reason, record.StartLine, record.EndLine)
}
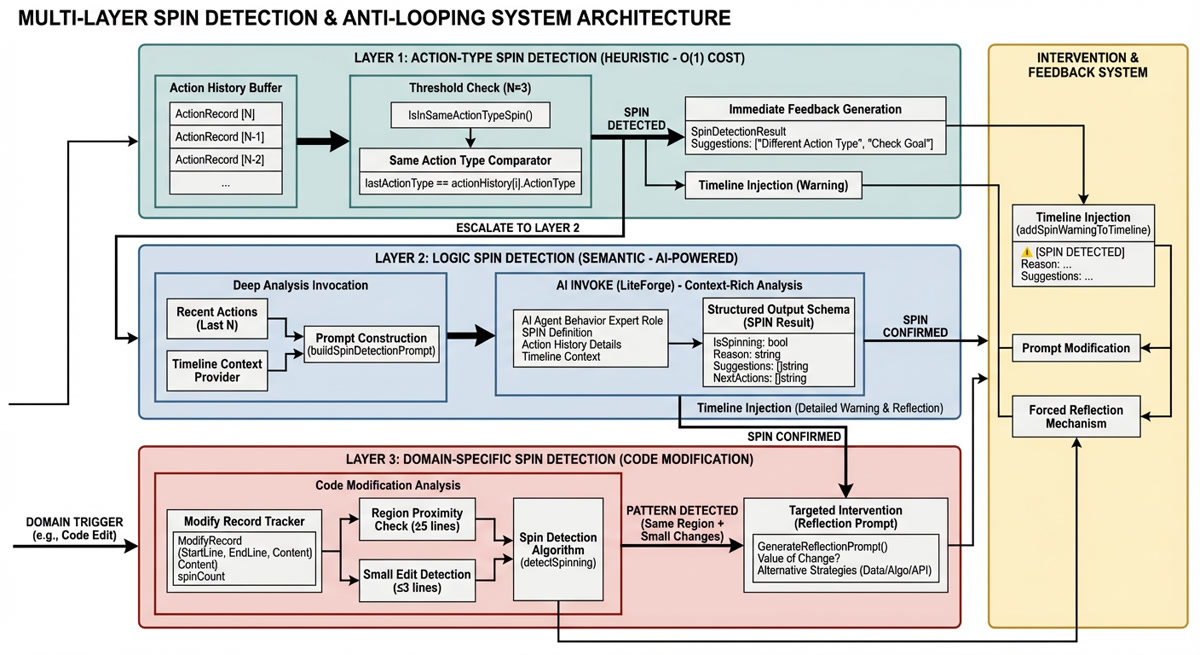
[图表占位符:多层 SPIN 检测架构]
- 布局: 带升级箭头的分层架构
- 层次:
- 第一层:启发式检测 (O(1) 成本,动作类型匹配)
- 第二层:语义检测 (AI 驱动,上下文分析)
- 第三层:领域特定 (专门用于代码、文件操作等)
- 升级路径: 第一层 → 第二层(触发时) → 第三层(领域特定)
- 干预点: 时间线注入、提示修改、强制反思
- 关键要点: 具有成本适当升级的渐进检测深度。
2.4 SPIN 警告注入
当检测到 SPIN 时,系统物理修改智能体的上下文:
// 来自 reflection.go - addSpinWarningToTimeline
func (r *ReActLoop) addSpinWarningToTimeline(reflection *ActionReflection) {
if !reflection.IsSpinning {
return
}
var msg strings.Builder
msg.WriteString("⚠️ [SPIN DETECTED] 检测到 AI Agent 陷入循环\n\n")
msg.WriteString(fmt.Sprintf("**Action 类型**: %s\n", reflection.ActionType))
msg.WriteString(fmt.Sprintf("**原因**: %s\n\n", reflection.SpinReason))
if len(reflection.Suggestions) > 0 {
msg.WriteString("**建议**:\n")
for i, suggestion := range reflection.Suggestions {
msg.WriteString(fmt.Sprintf("%d. %s\n", i+1, suggestion))
}
}
// 使用高优先级事件类型添加到时间线
invoker.AddToTimeline("logic_spin_warning", msg.String())
}
3. 记忆增强恢复
当智能体遇到问题时,它不仅仅依赖其预训练权重。它会查询长期向量记忆——过往任务的"黑匣子记录器"。
3.1 记忆实体结构
每个记忆都与丰富的元数据一起存储,实现复杂的检索:
// MemoryEntity 结构体(概念表示)
type MemoryEntity struct {
Id string `json:"id"`
Content string `json:"content"`
Tags []string `json:"tags"`
PotentialQuestions []string `json:"potential_questions"`
CreatedAt time.Time `json:"created_at"`
// C.O.R.E. P.A.C.T. 评分维度
C_Score float64 `json:"c_score"` // 关联度
O_Score float64 `json:"o_score"` // 来源
R_Score float64 `json:"r_score"` // 相关性
E_Score float64 `json:"e_score"` // 情感
P_Score float64 `json:"p_score"` // 偏好
A_Score float64 `json:"a_score"` // 可操作性
T_Score float64 `json:"t_score"` // 时效性
}
3.2 C.O.R.E. P.A.C.T. 评分框架
系统采用 7 维评分框架来评估记忆重要性和相关性:
| 维度 | 全称 | 权重 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| R | 相关性 (Relevance) | 0.25 | 对当前目标有多关键? |
| C | 关联度 (Connectivity) | 0.20 | 与多少其他记忆相连? |
| T | 时效性 (Temporality) | 0.15 | 应该保留多长时间? |
| A | 可操作性 (Actionability) | 0.15 | AI 能从中学习和改进吗? |
| P | 偏好 (Preference) | 0.10 | 是否绑定用户个人风格? |
| O | 来源 (Origin) | 0.10 | 来源可靠性? |
| E | 情感 (Emotion) | 0.05 | 用户的情绪状态? |
3.2.1 评分量表定义
每个维度使用归一化的 0.0-1.0 量表,具有语义范围:
T - 时效性:
0.0-0.3:瞬时记忆 - 仅对当前会话有效0.3-0.6:短期记忆 - 在数天/数周内有效0.6-0.8:中期记忆 - 稳定的偏好0.8-1.0:长期/核心记忆 - 不变的身份
A - 可操作性:
0.0-0.3:低价值 - 简单事实,无学习价值0.3-0.6:隐式反馈 - 行为模式0.6-0.8:显式反馈 - 用户直接评价0.8-1.0:可推广规则 - 未来的明确指示
C - 关联度:
0.0-0.3:孤立记忆 - 一次性事实0.3-0.6:线性关联 - 顺序关系0.6-0.8:主题节点 - 主题中的关键信息0.8-1.0:核心枢纽 - 连接多个领域
3.3 记忆检索管道
检索过程结合多种搜索策略:
// 来自 aimemory_search_memory.go - searchMemoryWithAIOption
func (t *AIMemoryTriage) searchMemoryWithAIOption(origin any, bytesLimit int, disableAI bool) (*SearchMemoryResult, error) {
var allMemories []*MemoryEntity
// 步骤 1:AI 驱动的标签选择
if !disableAI {
relevantTags, err = t.SelectTags(ctx, queryText)
}
// 步骤 2:基于标签的检索
if len(relevantTags) > 0 {
tagMemories, err := t.SearchByTags(relevantTags, false, 20)
allMemories = append(allMemories, tagMemories...)
}
// 步骤 3:语义相似性搜索
semanticResults, err := t.SearchBySemantics(queryText, 15)
for _, result := range semanticResults {
allMemories = append(allMemories, result.Entity)
}
// 步骤 4:去重
uniqueMemories := t.deduplicateMemories(allMemories)
// 步骤 5:C.O.R.E. P.A.C.T. 排序
rankedMemories := t.rankMemoriesByRelevance(uniqueMemories, queryText)
// 步骤 6:字节限制选择
selectedMemories, totalContent, contentBytes := t.selectMemoriesByBytesLimit(rankedMemories, bytesLimit)
return &SearchMemoryResult{
Memories: selectedMemories,
TotalContent: totalContent,
ContentBytes: contentBytes,
}, nil
}
3.4 相关性评分计算
排序算法结合 C.O.R.E. P.A.C.T. 分数与关键词匹配:
// 来自 aimemory_search_memory.go - calculateRelevanceScore
func (t *AIMemoryTriage) calculateRelevanceScore(memory *MemoryEntity, query string) float64 {
// C.O.R.E. P.A.C.T. 加权组合
weights := map[string]float64{
"R": 0.25, // 相关性 - 最重要
"C": 0.20, // 关联度
"T": 0.15, // 时效性
"A": 0.15, // 可操作性
"P": 0.10, // 偏好
"O": 0.10, // 来源
"E": 0.05, // 情感
}
relevanceScore := weights["R"]*memory.R_Score +
weights["C"]*memory.C_Score +
weights["T"]*memory.T_Score +
weights["A"]*memory.A_Score +
weights["P"]*memory.P_Score +
weights["O"]*memory.O_Score +
weights["E"]*memory.E_Score
// 关键词匹配加成(上限 0.3)
contentBonus := t.calculateKeywordBonus(memory, query)
return min(1.0, relevanceScore + contentBonus)
}
3.5 关键词匹配系统
关键词加成计算使用多种匹配策略:
// 来自 aimemory_search_memory.go - calculateKeywordBonus
func (t *AIMemoryTriage) calculateKeywordBonus(memory *MemoryEntity, query string) float64 {
contentBonus := 0.0
// 1. 内容关键词匹配(权重:0.1)
contentMatchScore := t.keywordMatcher.MatchScore(query, memory.Content)
contentBonus += contentMatchScore * 0.1
// 2. 标签关键词匹配(权重:0.08)
tagContent := strings.Join(memory.Tags, " ")
tagMatchScore := t.keywordMatcher.MatchScore(query, tagContent)
contentBonus += tagMatchScore * 0.08
// 3. 问题关键词匹配(权重:0.05)
questionContent := strings.Join(memory.PotentialQuestions, " ")
questionMatchScore := t.keywordMatcher.MatchScore(query, questionContent)
contentBonus += questionMatchScore * 0.05
// 4. 直接关键词存在(权重:0.05)
if t.keywordMatcher.ContainsKeyword(query, memory.Content) {
contentBonus += 0.05
}
// 5. 所有关键词匹配奖励(权重:0.03)
if t.keywordMatcher.MatchAllKeywords(query, memory.Content) {
contentBonus += 0.03
}
return min(0.3, contentBonus) // 上限 0.3
}
3.6 记忆去重系统
系统采用多维度去重方法:
// 来自 aimemory_triage_saving.go - BatchIsRepeatedMemoryEntities
func (t *AIMemoryTriage) BatchIsRepeatedMemoryEntities(entities []*MemoryEntity, config *DeduplicationConfig) ([]int, error) {
var nonRepeatedIndices []int
for i, entity := range entities {
// 维度 1:基于标签的重复(Jaccard 相似度)
tagRepeated, _ := t.checkTagRepetition(entity, config.TagOverlapThreshold)
// 维度 2:基于问题的重复(RAG 搜索)
questionRepeated, _ := t.checkQuestionRepetition(entity, config.QuestionSimilarityThreshold)
// 维度 3:基于内容的重复(语义相似度)
contentRepeated, _ := t.checkContentRepetition(entity, config.ContentSimilarityThreshold)
// 综合判断:2+ 维度匹配 = 重复
repetitionScore := 0
if tagRepeated { repetitionScore++ }
if questionRepeated { repetitionScore++ }
if contentRepeated { repetitionScore++ }
if repetitionScore < 2 {
nonRepeatedIndices = append(nonRepeatedIndices, i)
}
}
return nonRepeatedIndices, nil
}
3.6.1 去重配置
// DeduplicationConfig 带有合理默认值
type DeduplicationConfig struct {
TagOverlapThreshold float64 // 默认:0.8(Jaccard)
QuestionSimilarityThreshold float64 // 默认:0.85
ContentSimilarityThreshold float64 // 默认:0.9
}
3.7 从失败中学习
可靠性系统设计用于累积改进:
3.7.1 迭代后记忆处理
// 来自 re-act_mainloop.go - OnPostIteration 回调
func onPostIteration(loop *ReActLoop, iteration int, task AIStatefulTask, isDone bool, reason any) {
// 计算时间线差异
diffStr, err := config.TimelineDiffer.Diff()
if err != nil || diffStr == "" {
return // 没有新信息需要记录
}
// 上下文输入构建
contextualInput := fmt.Sprintf("ReAct迭代 %d/%s: %s\n任务状态: %s\n完成状态: %v\n原因: %v",
iteration,
task.GetId(),
diffStr,
string(task.GetStatus()),
isDone,
reason)
// 智能记忆处理(包含去重、评分、保存)
err = memoryTriage.HandleMemory(contextualInput)
}
3.7.2 任务完成记忆搜索
当任务完成时,系统主动搜索相关记忆:
// 已完成任务的记忆搜索(来自 coordinator_invoker.go)
if isDone {
go func() {
// 搜索与此任务相关的记忆(限制:4KB)
searchResult, err := memoryTriage.SearchMemory(task.GetUserInput(), 4096)
if err != nil {
return
}
if len(searchResult.Memories) > 0 {
log.Infof("found %d relevant memories for completed task %s",
len(searchResult.Memories), task.GetId())
// 记录记忆详情用于调试
for i, mem := range searchResult.Memories {
log.Infof("relevant memory %d: %s (C=%.2f, R=%.2f)",
i+1, mem.Content[:100], mem.C_Score, mem.R_Score)
}
}
}()
}
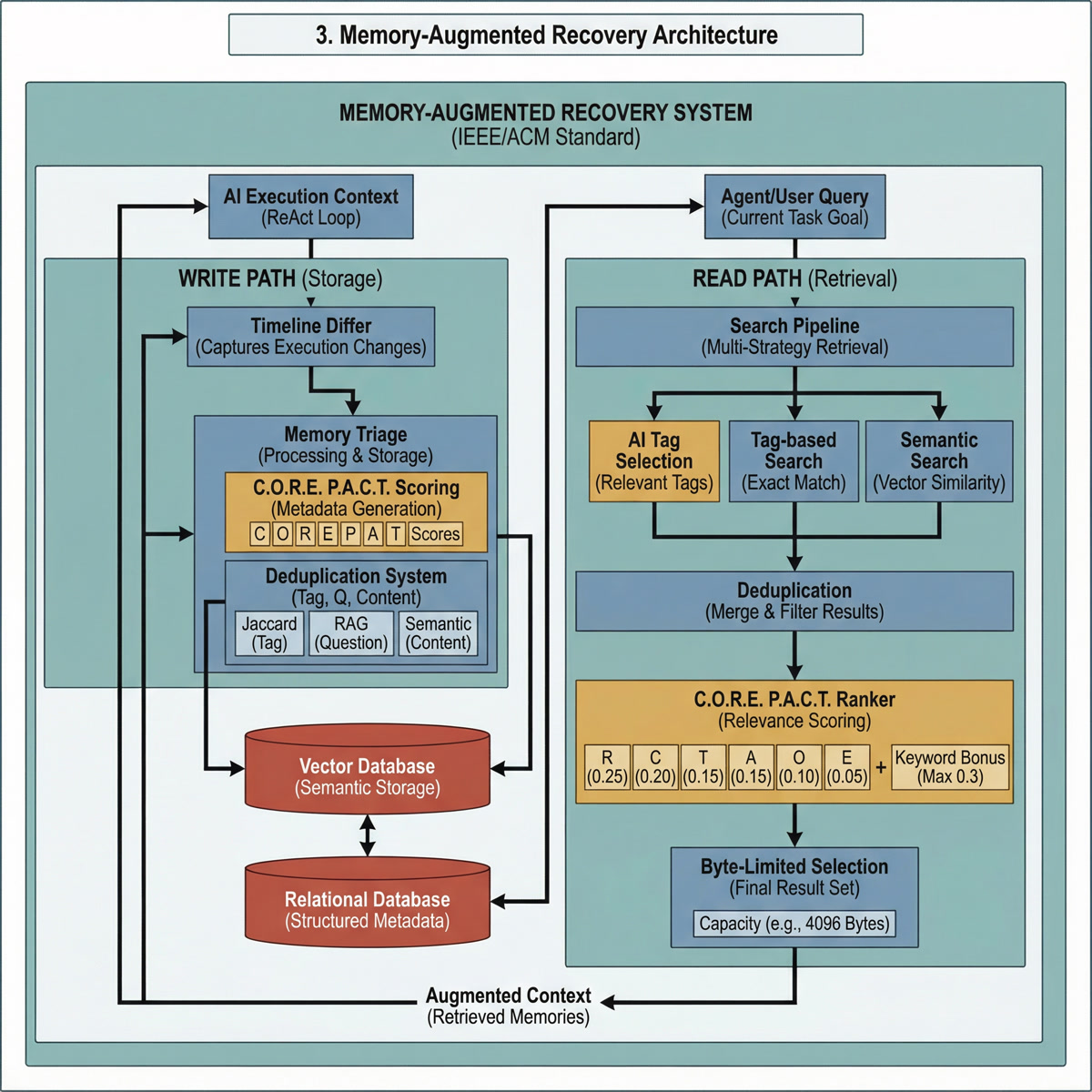
[图表占位符:记忆恢复架构]
- 布局: 带存储和检索路径的数据流图
- 组件:
- 时间线差异器 (捕获执行变化)
- 记忆分拣器 (处理和存储)
- 向量数据库 (语义存储)
- 关系数据库 (结构化元数据)
- 搜索管道 (多策略检索)
- C.O.R.E. P.A.C.T. 排序器 (相关性评分)
- 数据流:
- 写入路径:时间线 → 差异器 → 分拣器 → 去重 → 存储
- 读取路径:查询 → 标签 + 语义 → 去重 → 排序 → 选择
- 关键要点: 执行和记忆之间的双向流动。
4. 可靠性指标与监控
4.1 综合机制矩阵
| 机制 | 检测触发器 | 响应动作 | 计算成本 | 目的 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自我反思(Minimal) | 默认 | 仅记录 | O(1) | 执行跟踪 |
| 自我反思(Standard) | 迭代 > 5,SPIN | AI 分析 + 时间线注入 | O(n) API 调用 | 行为调整 |
| 自我反思(Critical) | 执行失败 | 完整根因分析 | O(n) API + 10KB 记忆 | 错误恢复 |
| 动作 SPIN(第一层) | Same(Action) × N | 立即警告 | O(1) | 打破机械循环 |
| 逻辑 SPIN(第二层) | 第一层触发 | AI 驱动分析 | O(n) API 调用 | 打破认知僵局 |
| 领域 SPIN(第三层) | 同一区域 × 3 | 专门干预 | O(1) | 领域特定恢复 |
| 记忆恢复 | 新任务 / 失败 | 向量搜索 + 排序 | O(log n) 搜索 | 经验重用 |
| 去重 | 记忆保存 | 多维度检查 | O(n²) 比较 | 存储效率 |
4.2 级联防御策略
可靠性机制形成级联防御:
级别 0:最小反思(始终开启)
↓(失败或迭代 > 5 时)
级别 1:标准反思 + 第一层 SPIN 检测
↓(SPIN 触发时)
级别 2:AI 驱动的逻辑分析
↓(领域特定模式时)
级别 3:专门干预
↓(始终)
级别 4:记忆增强恢复
4.3 关键可靠性保证
- 无静默失败:每个执行错误至少触发
Critical反思。 - 循环终止:多层 SPIN 检测确保在 N 次迭代内检测到循环(可配置,默认 N=3)。
- 上下文保留:所有重要事件都记录到时间线,并可选持久化到长期记忆。
- 渐进降级:随着可靠性机制激活,计算资源按比例扩展。
- 跨会话学习:记忆实体跨会话持久化,实现持续改进。
5. 结论
Memfit AI 可靠性架构代表了既定软件工程原则与新型 AI 特定机制的综合。通过以下组合:
- 分级反思级别:用于成比例的诊断深度
- 多层 SPIN 检测:用于全面的循环预防
- C.O.R.E. P.A.C.T. 记忆框架:用于智能经验检索
- 基于时间线的上下文注入:用于行为指导
系统实现了超越传统 AI 智能体实现的运行可靠性水平。该架构不仅仅是为了预防故障,而是为了从中学习,建立随时间推移提高可靠性的累积知识库。
这种纵深防御方法确保 Memfit AI 能够在不可预测的真实世界环境中稳健运行,优雅处理错误,避免无限循环,并利用过去的经验应对新挑战。